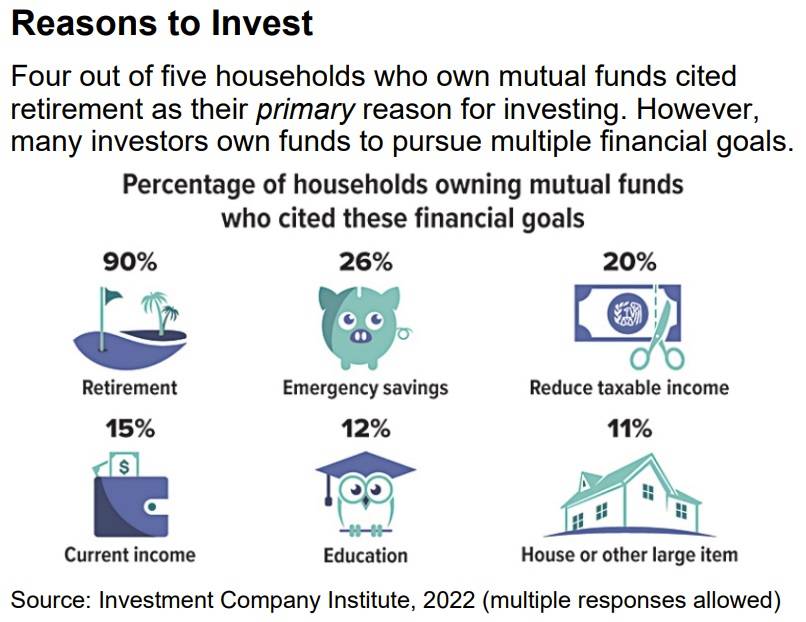
Mutual funds pool investment dollars from many individual investors to purchase a group of selected securities aimed at meeting a particular objective. This offers a convenient way to invest across a wide range of market activity that would be difficult for most investors to do by purchasing individual securities. More than 52% of U.S. households owned mutual funds in 2022.1
Here are some basic types of funds in order of typical risk, from lowest to highest. This is just an overview — with over 7,000 funds to choose from, you should be able to find appropriate investments to pursue your financial goals.2
- Money market funds invest in short-term debt such as commercial paper and certificates of deposit (which generally provide a fixed rate of return). They are typically used as a cash alternative and/or as a fund for settling brokerage transactions.
- Municipal bond funds generally offer income that is free of federal income tax and may be free of state income tax if the bonds in the fund were issued from your state. Although interest income from municipal bond funds may be tax exempt, any capital gains are subject to tax. Income for some investors may be subject to state and local taxes and the federal alternative minimum tax.
- Income funds concentrate on bonds, Treasury securities, and other income-oriented securities, and may also include stocks that have a history of paying high dividends.
- Balanced funds, hybrid funds, and growth and income funds seek the middle ground between growth funds and income funds. They include a mix of stocks and bonds aimed at combining moderate growth potential with modest income.
- Value funds invest in stocks of companies that appear to be undervalued by the market. They are more volatile than balanced funds, but typically offer dividend income and may have solid growth potential if the market recognizes the underlying value.
- Growth funds invest in the stock of companies with a high potential for appreciation but low emphasis on income. They are more volatile than many types of funds.
- Global funds invest in a combination of domestic and foreign securities.
- International funds invest primarily in foreign stock and bond markets, sometimes in specific regions or countries. There are increased risks associated with international investing, including differences in financial reporting, currency exchange risk, economic and political risk unique to a specific country, and greater share price volatility.
- Sector funds invest almost exclusively in a particular industry or sector of the economy. Although they offer greater appreciation potential, the volatility and risk level are also higher because they are less diversified.
- Aggressive growth funds aim for maximum growth. They typically distribute little income, have very high growth potential, tend to be more volatile, and are considered to be very high risk.
Bond funds (including funds that contain both stocks and bonds) are subject to the interest-rate, inflation, and credit risks associated with the underlying bonds. As interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, which can adversely affect a bond fund’s performance. U.S. Treasury securities are guaranteed by the federal government as to the timely payment of principal and interest. Dividends are typically not guaranteed.
Asset allocation and diversification are methods used to help manage investment risk; they do not guarantee a profit or protect against investment loss. Mutual fund shares, when sold, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Investments seeking to achieve higher returns also carry an increased level of risk.
Money market funds are neither insured nor guaranteed by the FDIC or any other government agency. Although a money market fund attempts to maintain a stable $1 share price, you can lose money by investing in such a fund.
Mutual funds are sold by prospectus. Please consider the investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses carefully before investing. The prospectus, which contains this and other information about the investment company, can be obtained from your financial professional. Be sure to read the prospectus carefully before deciding whether to invest.
1–2) Investment Company Institute, 2022–2023
Prepared by Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. Copyright 2023